How to Make a Database for Small Business Company
In order to make a database for your organization, you will need to know how to organize, use and manage your small business information. A database made and tailored to your specific needs allows you to maximize the value of your business through data integration and access. All business activities can be integrated and recorded in a single database: payments, sales, performance, projects and other essential details of your firm.
Benefits of Making a Database for Business
If you ever want to create a client base, a document archive, an article directory or another kind of digital repository in which business information is structured and indexed, you need to know about managing database - driven business activities. Databases serve as the main tool to collect, retain, update and extract business data. For example, a customer database lets you make records on your clients, create customer profiles, retain business contacts, save account history, and retrieve information about a customer's latest activity.
How to Make a Database?
Database building and management may seem like a daunting and expensive task at first if you have never done it before. Nevertheless, when you know what benefits your company derives from a well-made database, you will likely be ready to invest your money and time in turning your small business activities into database-driven tasks.
Here are the greatest benefits your business can gain:
- Enter and store vast amounts of information about your products or services
- Retrieve the data with ease and when needed
- Separate business activities from each other so that you can focus on the details of one or another activity
- Keep and update business records on your personnel, clients, suppliers, partners, etc.
- Track history of changes in the database
- Protect and secure your business data
- Organize and search records
- Enhance user interactivity and collaboration
Which of Two Database Types to Use
In general, there are two types of database including Flat and Relational. For both types, tables serve as the building blocks to organize and index information. Your ultimate task is to understand the benefits of each database type and select the best one for your business.
Flat Database Design
A flat-type database has a simple design consisting of one large table with two dimensions (fields and records). A great example of this type is Excel spreadsheet in which data is entered in cells made of rows and columns. MS Excel and other spreadsheet apps represent simple data relationships, so flat databases are best for simple data manipulations, for example you can make data calculations and visualization in Excel spreadsheet.
Relational Database Design
A relational database represents a complex design in which all data is stored in relations and organized by multiple tables. These relations allows database users to access the data in almost any way and to use tables and their records, fields and values for creating and customizing large databases. As an example, Access, Oracle, CentriQS and other relational database systems let create databases to keep vast amounts of business data organized by multiple tables with numerous records and fields. So, if you want all of your business data to be stored and organized in one place, you should select a relational database system. Below you can see how to make your database in CentriQS relational database management software.
Creating a Database in CentriQS
How to make a database in CentriQS? To answer this question, first of all you need to select a database customization solution and then follow certain procedures. For example, you can select CentriQS software which lets create and configure databases for small business. In CentriQS database builder you can create custom entities, properties, workflows, and tables to make your database fitting your company's requirements.
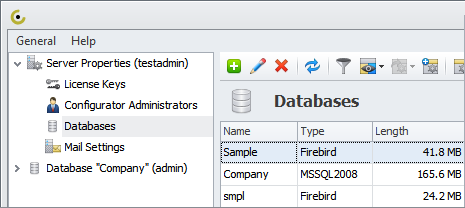
You can follow these five steps to create a database in CentriQS database design tool:
1. Add Custom Entities
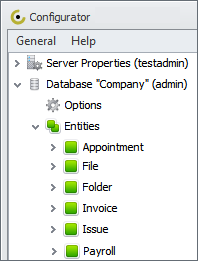
Any database made in CentriQS Configurator consists of default entities (or objects) that help users manage typical business activities. In particular, default entities are Task, Project, Appointment, Folder, File, User, and others. If you want to tailor your business data to your specific needs you need to add custom entities. For example, you can create such entities as Customer, Payroll, Invoice, and others. These objects will let add customers, payroll details and payments to your database.
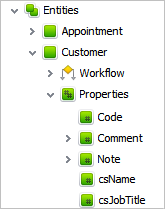
2. Set Properties for Custom Entities
Each of the custom entities you added to your database includes a number of default properties such as Title, Code, Note, History, and so on. Creating custom properties will help you specify each custom entity by certain details; for example, the Invoice entity may include these custom properties: Payment Date, Amount, Tax, Payer, and Ref#.
3. Create Relationships between Database Entities
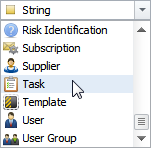
All default and custom entities can be related to each other. For example, the default entity 'Task' can be related to the custom entity 'Customer'. This relationship between the entities allows you to view which tasks relate to one or another customer in your database. Essentially, entity relationships make your database much bespoken and tailored to your unique small business needs.
4. Set Entity Workflows
When you make a database, you can set one workflow for default or custom entity. Entity workflow creates progression of steps that comprise a process and relate to a certain business object. For instance, the sales process includes a number of steps and relates to the custom entity 'Customer'. By adding workflow you can adjust your database to the business processes of your company.
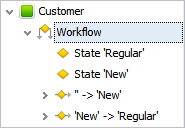
5. Arrange Entity Data by Tables
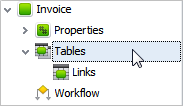
In order to program your database more completely and comprehensively, you can use tables that arrange quantitative data of entities in rows and columns. In particular, tables let make calculations for one or more entities or their properties. For example, for the object "Invoice" you can create the table "Purchases" that shows lists all purchases relating to a given invoice sample. This table helps you quickly calculate amounts of purchases in your invoices.
Prev.: FileMaker vs Access Review for Small Business || Next: Key Reasons for Searching Microsoft Access Alternative
Next steps
{
Check out CentriQS FEATURES & SCREENSHOTS
Watch 7-minute CentriQS VIDEO OVERVIEW
Learn how to use CentriQS in KNOWLEDGE BASE
DOWNLOAD CentriQS 30-day Free Trial Version
CONTACT US to get help with CentriQS Database Design & Configuration